Introduction
Today, deliveries are fast and customer demands keep rising. Factories must work smarter, not just harder. Competition is fiercer than ever, and delays can cost a company its reputation.
Enhancing the manufacturing process is not merely an added benefit; it’s crucial, for survival. It involves reducing expenses and enhancing customer satisfaction to achieve results. This article looks at how factories can change their production lines. It helps them reach peak performance and long-term success.
What Are the Common Bottlenecks in Factory Production?
Before you can fix a process, you have to understand what’s slowing it down. Bottlenecks are those sticky points in production where everything grinds to a halt. These problems often hide in plain sight: outdated machines, confusing floor layouts, or schedules that can’t keep up with changing orders. Understanding them is step one toward making real progress.
1. Common Process Bottlenecks
Poor layouts often mean materials have to travel long distances, wasting time and energy. Equipment failures cause unexpected downtime, and rigid schedules can’t adjust when orders pile up or change suddenly.
|
Common Bottleneck |
Description |
Impact |
|
Poor Line Layout |
Long transport routes between steps |
Increased cycle time |
|
Frequent Breakdowns |
Equipment prone to failure |
Lower output and higher costs |
|
Inflexible Planning |
Slow to adapt to order changes |
Missed deadlines |
2. Resource Waste and Efficiency Loss
Even when production seems steady, hidden inefficiencies pile up. Some factories sit on massive stockpiles while simultaneously running out of key materials. Others suffer from machines and workers sitting idle, costing money every minute. Issues, with quality often result in the need to redo work and discard both time and materials.
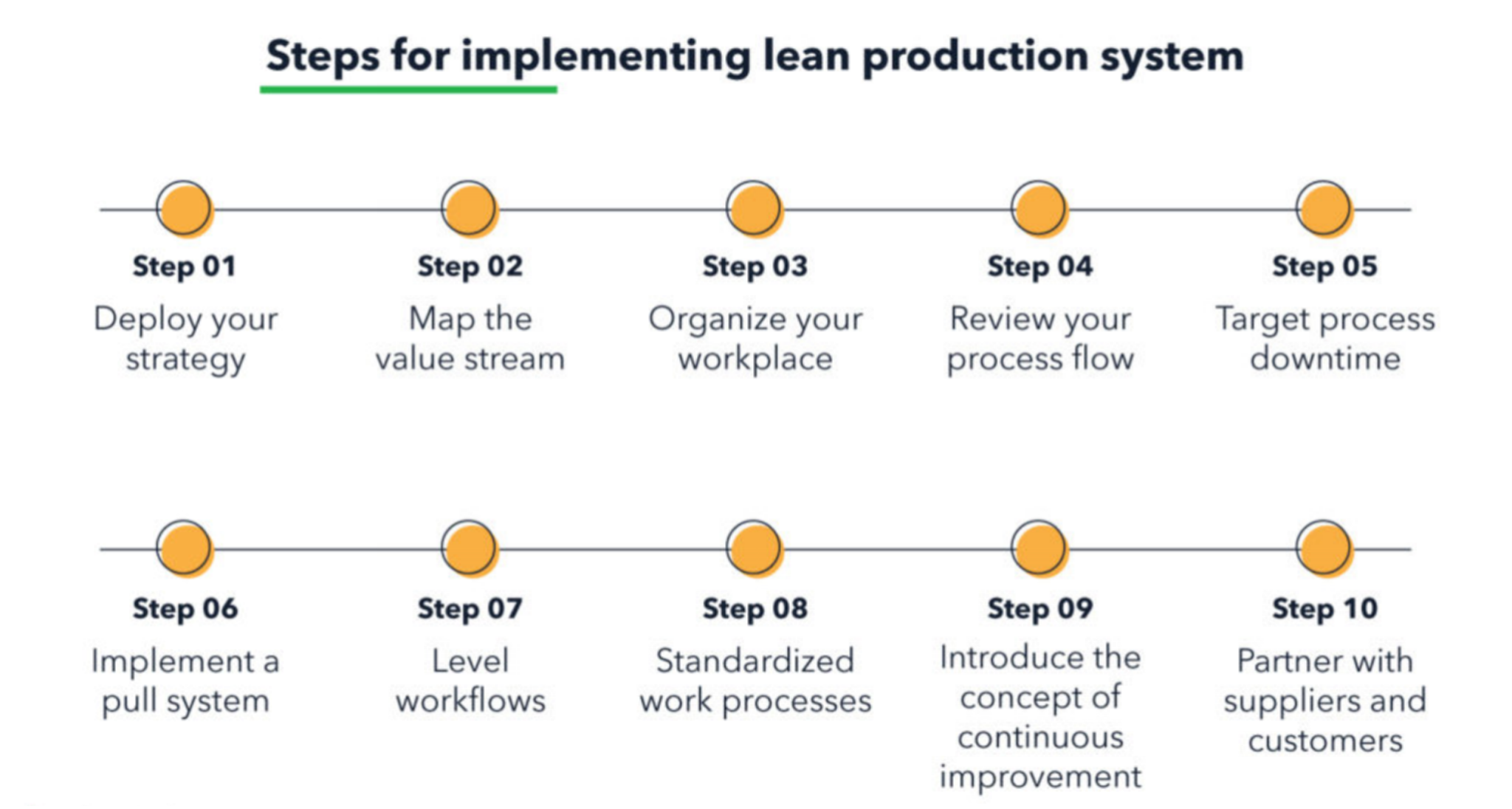
How Can Lean Manufacturing Enhance Efficiency?
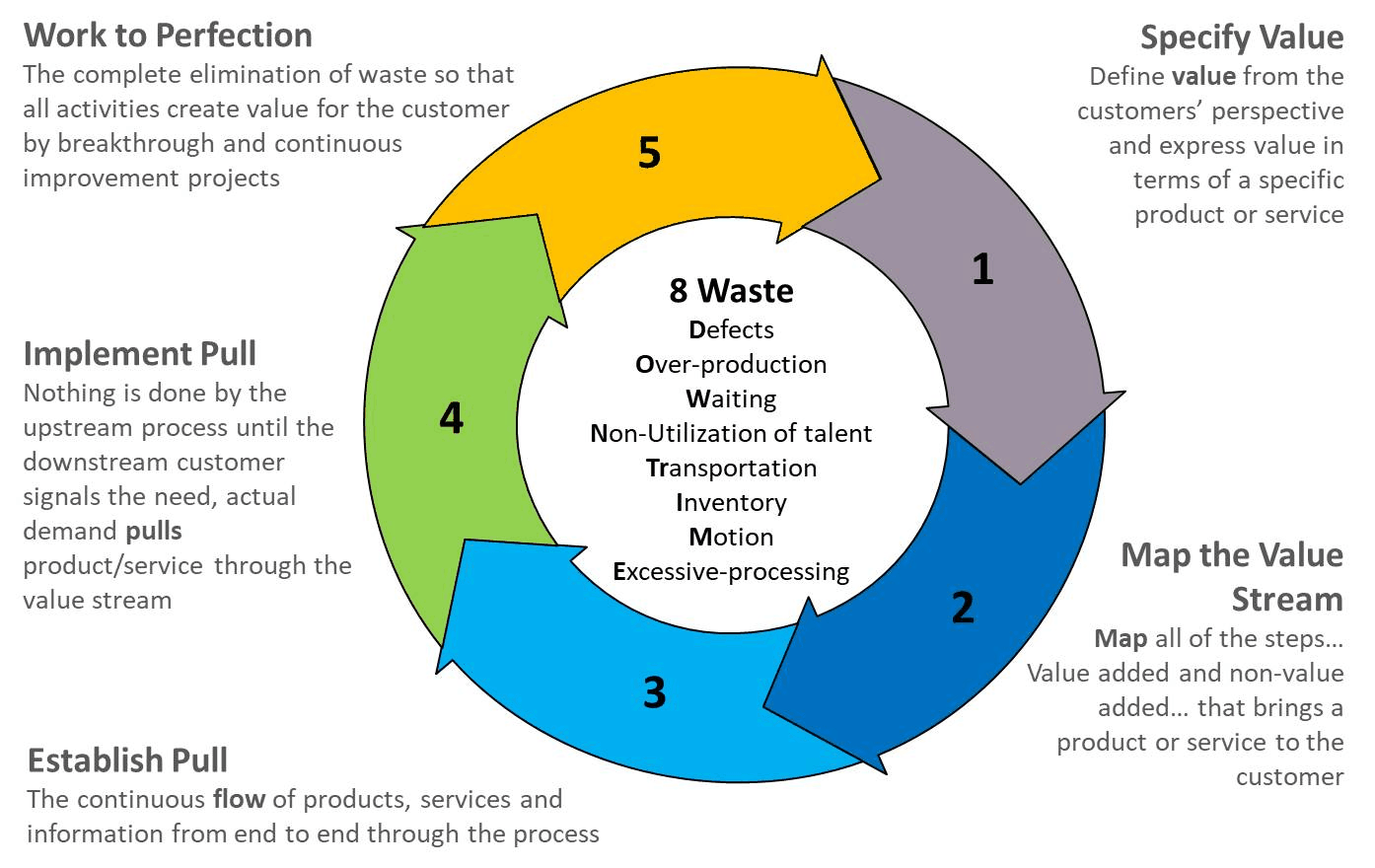
When aiming to enhance productivity levels in a business setting – lean manufacturing stands out as a tested method. It doesn’t just cut out the extras. It helps every step of production work smoother and smarter. Lean helps you build systems that do more with less, respond faster to change, and eliminate the kinds of waste that quietly drain profits.
1. Lean Applications
Eliminating waste isn’t just a buzzword. The “eight wastes” lean identifies—like overproduction and waiting—are real profit killers. Quick-change systems (SMED) help factories switch products faster, and unit production lines mean parts move without delays.
|
Lean Strategy |
How It Helps |
|
SMED |
Reduces downtime during product changeovers |
|
One-Piece Flow |
Cuts down on waiting and inventory buildup |
|
Eliminate Seven Wastes |
Boosts overall productivity |
2. Standardization and Flexibility
Flexibility doesn’t mean chaos. It means creating smart, repeatable processes that allow easy adjustments. SOPs ensure every worker knows the right way to do things. Modular designs let factories handle multiple product types without slowing down.
What Specific Measures Reduce Customer Waiting Time?
Meeting customer expectations for fast and reliable delivery is no longer optional. It’s required. To stay ahead, manufacturers must look at every part of their process and ask: how can we do this faster without cutting corners? Smart planning can help factories cut lead times. Faster workflows and clear communication can also boost customer satisfaction.
1. Production Planning Optimization
Modern planning systems like APS (Advanced Planning and Scheduling) use real-time data to juggle priorities. They reroute resources. Important requests can transition smoothly into the production process without creating any disruptions.
|
Production Planning Strategy |
Benefit |
|
Dynamic Scheduling (APS) |
Real-time responsiveness to changes |
|
Priority Management |
Ensures urgent jobs are prioritized |
2. Production Cycle Time Reduction
Reducing cycle times doesn’t involve taking shortcuts; it involves eliminating inefficiencies and unnecessary steps in the process. Designing for parallel processing lets tasks happen at the same time. Choosing One-Piece Flow or Continuous Flow Manufacturing cuts delays and speeds things up.
3. Customer Collaboration Management
Keeping customers in the loop builds trust. A transparent order tracking system lets them see exactly where their products are. Batch deliveries help fulfill immediate needs while final touches are still in progress.
What Steps and Safeguards Ensure Successful Implementation?
Even the best ideas fall flat without a clear plan. Turning optimization goals into real results requires a structured approach. It also means getting everyone on board—from line workers to top management. With the right tools, clear communication, and cultural buy-in, process improvements can become lasting gains.
1. Optimization Steps
Start with a diagnosis: map out the current process (Value Stream Mapping, VSM) to find the biggest problems. Test improvements in small areas first, then roll them out company-wide once proven.
2. Organizational and Cultural Support
Process changes don’t work if teams aren’t on board. Success depends on creating cross-departmental collaboration (production, purchasing, warehousing) and promoting a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen).
3. Technical Tools Support
Tools like Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software help coordinate every aspect of production. Big data analysis predicts equipment issues and demand swings, letting teams fix problems before they start.
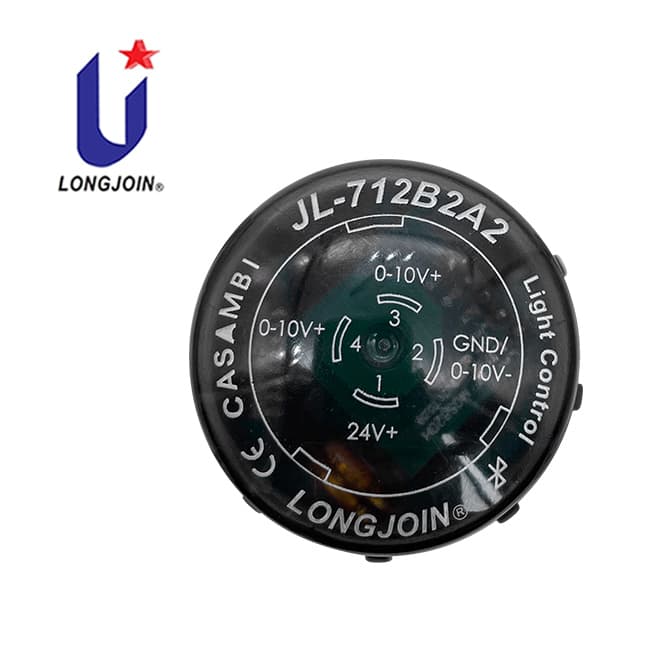
How Do Photocell Sensors Contribute to Production Optimization?
Modern factories are smarter than ever. One of the technologies making this possible is the photocell sensor. It might be small, but its impact is big. These sensors help automate tasks. They cut down on wasted energy and keep places safe. Their role in lighting and equipment control can quietly add up to major gains in efficiency and cost savings.
Benefits of Photocell Sensors:
- Automation: Automatically control lights and machines based on environmental conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: Slash electricity bills by running equipment only when needed.
- Safety: Ensure well-lit workspaces without relying on manual checks.
Practical Applications:
- Lighting Control: Adjust brightness automatically using light sensor photocell switches.
- Equipment Activation: Machines turn on/off depending on light levels, saving both energy and wear.
Integration with Smart Systems: Today’s photocell systems, like the ones at Long-Join, integrate with smart monitoring to allow:
- Remote light and machine monitoring.
- Data collection for predictive maintenance.
Conclusion
Optimizing a factory’s production process is no passing fad. It’s our future. Companies that spot bottlenecks and use lean strategies embrace smart tools like photocell sensors. A culture of constant improvement will let them lead the way.New trends like Industry 4.0, AI-driven decisions, and green manufacturing will help factories work better and use less energy. Staying ahead means starting now.
External Links:
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/erp.asp
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manufacturing_execution_system
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kaizen
- https://www.lean.org/lexicon-terms/value-stream-mapping/
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchbusinessanalytics/definition/standard-operating-procedure-SOP
- https://www.leanproduction.com/smed/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_planning_and_scheduling
Post time: Apr-30-2025